Asilata Karandikar is a PhD student at Centre for Information Technology and Public Policy, and the Web Science Lab, at IIIT Bangalore. Prior to joining here, she taught Political Science at Wilson College, Mumbai, and has also worked as a Research Associate at the Centre for Enquiry into Health and Allied Themes, Mumbai. Her current project deals with questions of privacy and consent from a social-contractual perspective.
CIKM 2023 Workshop on Enterprise Knowledge Graphs Using Large Language Models
22nd October 2023,University of Birmingham, UK

Contact Us
Rajeev Gupta (Principal scientist, Microsoft, India)
Microsoft R&D India Pvt. Ltd., Hyderabad, India
Email: [email protected]
CIKM 2023 Workshop on Enterprise Knowledge Graphs Using Large Language Models
22nd October 2023,University of Birmingham, UK

Programme Committee
- Manoj Agarwal (Senior Researcher, Discovery Intelligence, Uber Research)
- Manish Bhide (CTO, AI Governance, IBM)
- Mukesh Mohania (Professor, CSE, IIIT Delhi)
- Prasad Deshpande (Senior Staff Software Engineer, Databricks)
- Qi He (Head of AI, Nextdoor)
- Ranganath Kondapally (Principal Applied Scientist, Microsoft)
- Rushi Bhatt (Partner, ML Systems and Services, Microsoft)
- Sauvik Ghosh (Director of AI, LinkedIn)
Workshop Chairs
- Rajeev Gupta (Principal scientist, Microsoft, India): [email protected]
- Srinath Srinivasa (Professor and Dean (R&D), Web Science Lab, IIIT-Bangalore): [email protected]
Website Chairs
- Bhoomika A P, PhD Scholar, WSL, IIIT-Bangalore :[email protected]
- Aparna M, M.S Scholar, WSL, IIIT-Bangalore: [email protected]
CIKM 2023 Workshop on Enterprise Knowledge Graphs Using Large Language Models
22nd October 2023,University of Birmingham, UK

Workshop Schedule
Workshop Venue: Teaching and Learning Building (M208/M209) at the University of Birmingham (workshop venue).
The below schedule is based on UK time zone(UTC+1).
Session 1: 9.00-10.30
| Introduction & Initial announcements: 9.00-9.30 |
| Lessons from the age of user-generated content for the age of AI-generated content (Prof. Nishanth Sastry: 9.30 to 10.30 ) |
| Refreshment Break: 10:30-11:00 |
Session 2: 11.00-12.30
| Enhancing Enterprise Knowledge Base Construction with Fine-Tuned Generative Language Models (Liana Mikaelyan:11.00-11.45) |
| Research Session 1: 11.45 – 12:30 1. Related Table Search for Numeric data using Large Language Models and Enterprise Knowledge Graphs(Pranav Subramaniam, Udayan Khurana, Kavitha Srinivas and Horst Samulowitz) 2. Cognitive Retrieve: Empowering Document Retrieval with Semantics and Domain Specific Knowledge Graph(Apurva Kulkarni, Chandrashekar Ramanathan and Vinu E Venugopal) |
| Lunch: 12.30- 14.00 |
Session 3: 14:00- 15:30
| Building Knowledge Graph for Products at Scale and infusing it into LLMs(Dr. Manoj Agarwal: : 14.00-14.45) |
| Research Session 2:(14.45 -15.30) 1. EduEmbedd – A Knowledge Graph Embedding for Education(Anurag Mohanty) 2. CRUSH: Cybersecurity Research using Universal LLMs and Semantic Hypernetworks (Mohit Sewak, Vamsi Emani and Annam Naresh) |
| Refreshment Break: 15.30 – 16.00 |
Session 4: 16.00- 17:00
| LLMs for Social Networks: Applications, Challenges and Solutions (Bojan Babic: 16.00-17.00) |
CIKM 2023 Workshop on Enterprise Knowledge Graphs Using Large Language Models
22nd October 2023,University of Birmingham, UK

Important Dates
| Abstract Submission: |
| Paper submission : |
| Notification of paper acceptance : |
| Camera Ready Paper Submission : 1st October 2023 |
| The workshop : 22nd October 2023 |
CIKM 2023 Workshop on Enterprise Knowledge Graphs Using Large Language Models
22nd October 2023,University of Birmingham, UK

Invited Talks
Lessons from the age of user-generated content for the age of AI-generated content

Prof. Nishanth Sastry, Director of Research of the Department of Computer Science, University of Surrey.
Abstract:
The past decade and more has been defined by the rise and near universal adoption of user-generated content (UGC) on social media. Initial excitement about the promise of UGC has since become tempered by concerns about misinformation, hate speech and other online harms. We are now witnessing a similar enthusiasm for content generated by Large Language Models. This talk will draw parallels between the two, and extract lessons about the perils, potentials and pitfalls awaiting us in the future age of AI-generated content.
Biography:
Prof. Nishanth Sastry is the Director of Research of the Department of Computer Science, University of Surrey. His research spans a number of topics relating to social media, content delivery and networking, and online safety and privacy. He is joint Head of the Distributed and Networked Systems Group and co-leads the Pan University Surrey Security Network. He is also a Surrey AI Fellow and a Visiting Researcher at the Alan Turing Institute, where he is a co-lead of the Social Data Science Special Interest Group.
Can machines discover new knowledge?
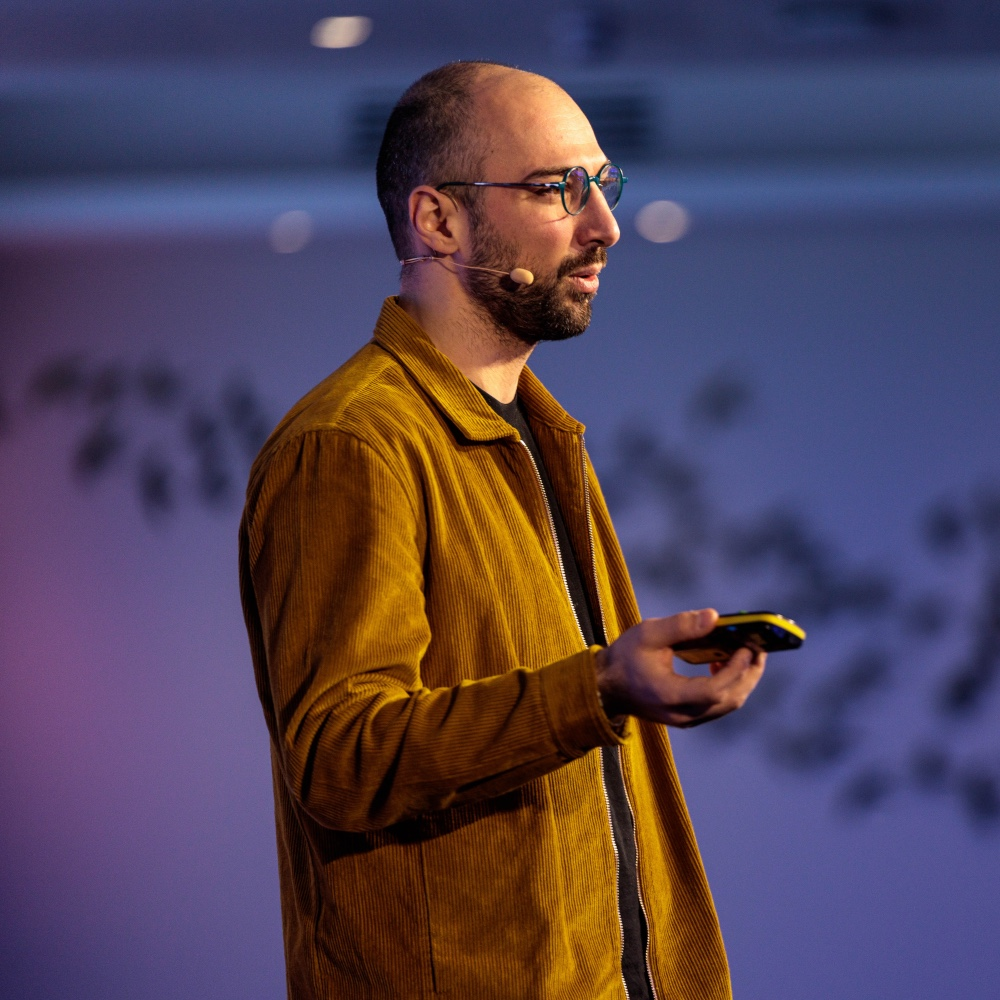

Dr. Fabio Petroni, Co-Founder & CTO at Samaya AI
Abstract:
For many years, the quest to determine the most efficacious representations of knowledge for machines has been at the forefront of research. Historically, this focus has centered on knowledge retrieval, whether from unstructured text corpora, structured collections (e.g, knowledge graphs, key-value memories), or the parameters of a neural model. How can we evolve these representations to not just retrieve, but actively discover new knowledge?
Biography:
Dr. Fabio Petroni is the Co-Founder & CTO at Samaya AI, building an AI-powered knowledge-discovery platform. Before that he was a Researcher at FAIR and Thomson Reuters, focusing on representing, gathering, extracting, using, reasoning on and creating world knowledge using AI.
Enhancing Enterprise Knowledge Base Construction with Fine-Tuned Generative Language Models
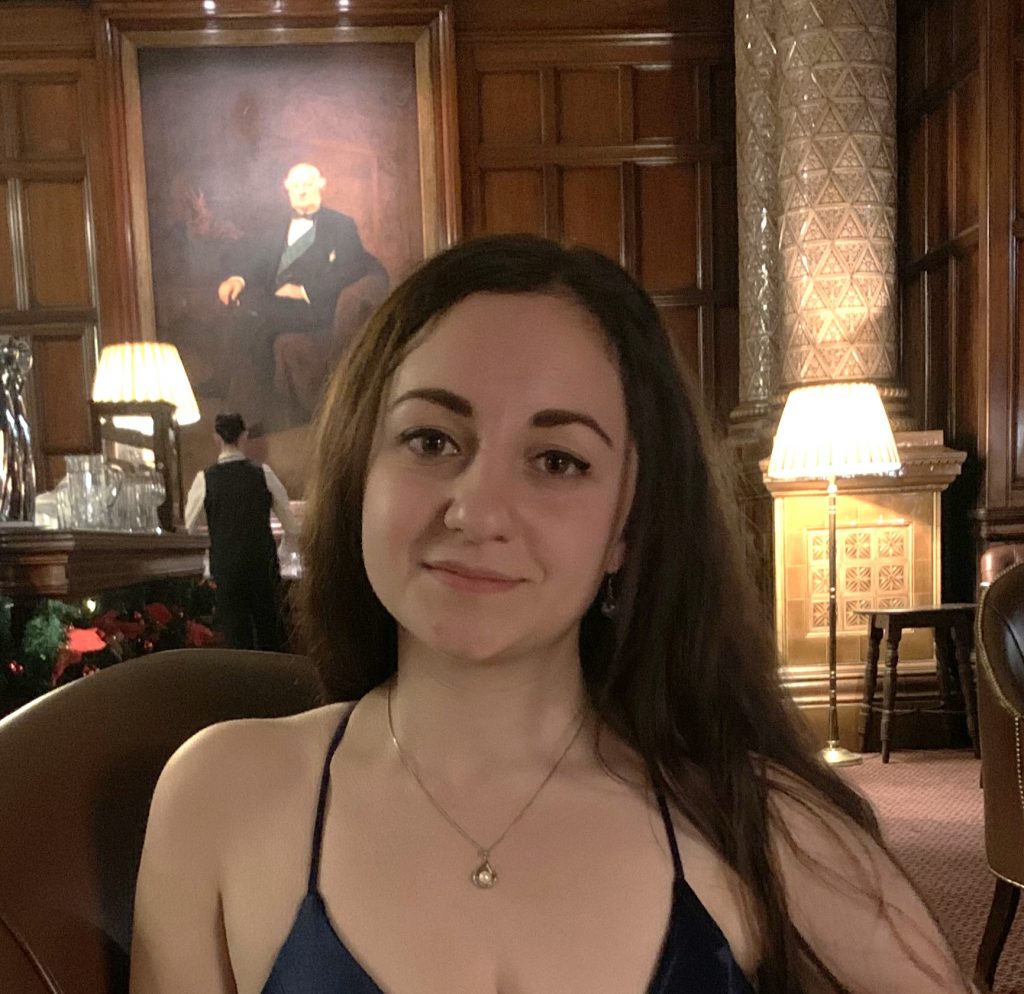

Ms. Liana Mikaelyan, Research Software Development Engineer in the Alexandria team, Microsoft Research Cambridge UK .
Abstract:
In this talk, we will present our latest work on leveraging the power of generative language models for knowledge base construction. We have fine-tuned a generative LLM to extract entities and their relevant properties from text passages and represent them in a structured JSON format. This task was accomplished by creating a dataset of short passages and corresponding JSON outputs using GPT4, which was then used to fine-tune the OpenLlama 3B model on a single A100 GPU. Our approach has demonstrated superior performance compared to the existing template matching algorithm in Alexandria, both in terms of precision and coverage, as well as extracting a richer set of properties from the text. Furthermore, the addition of new properties to the knowledge base has been significantly simplified. Future work involves exploring ways to improve the generation time as well as investigating other models to further enhance our system’s performance
Biography:
Ms. Liana Mikaelyan is a Research Software Development Engineer in the Alexandria team at Microsoft Research Cambridge UK . Before joining Microsoft Research Cambridge she worked on various machine learning projects mainly in speech synthesis and recognition. She completed her MSc in Machine Learning at UCL with a background in mathematics.
LLMs for Social Networks: Applications, Challenges and Solutions

Bojan Babic, Nextdoor.
Abstract:
Last couple of years we have witnessed an explosion of Generative AI research and respective applications that are simultaneously transforming how companies operate internally and how they communicate with their customers.
In this talk we will present work of the Nextdoor GenAI team and respective LLM applications in social networks in the areas such as Knowledge tasks, Engagement tasks and Governance. We will cover what we have tried, what works and what does not work. At the same time, in this talk we will present a framework that we used that helped us iterate fast and systematically improve each of the product areas.
Biography:
Bojan Babic is currently working on various Generative AI problems at the social media platform Nextdoor. Preceding this position, he has been working on the Search/Information Retrieval, Ads and recommendations and respective application spanning from e-commerce to social media space
Building Knowledge Graph for Products at Scale and infusing it in to LLMs

Dr. Manoj Agarwal,Senior Staff Engineer in Discovery Intelligence team at Uber AI.
Abstract:
A knowledge graph is the key to entity search as it can store the factual entity related information in a structured manner without the rigidity of a fixed schema. Both Google and Bing have web scale knowledge graphs and for a large fraction of user queries knowledge graph is invoked. E-commerce search is primarily an entity search. Therefore, building a Knowledge Graph is the key to improve the eCommerce search in many ways. However, building it at web scale is a highly challenging problem. It is an equally or even more challenging problem to build the knowledge graph for products. In this talk, we present our methodology to build the knowledge graph for products at web scale. With recent success of LLMs, can we infuse such semantic understanding of the world, encoded in the form of Knowledge Graph, in the LLMs? There are some advances in this direction, however it remains an open question if the Knowledge graphs can be replaced by the LLMs.
Biography:
Dr. Manoj Agarwal is Senior Staff Engineer in Discovery Intelligence team at Uber AI. Before Uber, he was Principal Applied Scientist at Microsoft – AI and Research and a senior researcher in IBM Research. Manoj was the chief architect for building a web scale product knowledge graph for Microsoft – Shopping, comprising a few hundred million products and a few billion facts with high accuracy. Currently, he is engaged in the efforts to build the scalable knowledge graph as well as discovering the taxonomy to improve the semantic search and recommendations for Uber Delivery. His research interests are in the areas of web mining, graph mining, pattern recognition, data mining, knowledge graphs, LLMs and information retrieval with more than 30 patents and over 25 research papers in reputed journals and conferences.
CIKM 2023 Workshop on Enterprise Knowledge Graphs Using Large Language Models
22nd October 2023,University of Birmingham, UK

Call For Papers
Knowledge graphs can integrate diverse data sources and provide a holistic view to the downstream applications. By virtue of being structured, knowledge graphs offer transparency and interpretability to the search and recommendations applications. Combining Knowledge Graphs with current-day advances in LLMs can create several opportunities.
The EKG-LLM workshop as part of CIKM 2023, would be addressing how large language models can help with the construction and usage of these enterprise knowledge graphs. This involves improving all the aspects of EKG workflow using large language models: entity extraction, entity enrichment, EKG construction, querying EKG for search and recommendations, scenario specific EKG, etc. Through this workshop we would like to highlight research issues specific to the integration of the enterprise knowledge graphs with large language models and associated applications.
Topics of interest include but are not limited to, the following:
- Designing Enterprise Knowledge Graph (EKG)
- EKG Implementation
- Scalable extraction of enterprise entities using LLMs
- Building EKGs for specific domains or applications
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) algorithms to build EKGs.
- Relationship extraction using large language models
- Federated graph learning with LLMs
- Privacy in graph algorithms
- Privacy preserving graph construction and mining
- Semantic reasoning based on deep learning on graph
- Industrial applications of EKGs: banking, financing, retail, healthcare, medicine, etc.
- Explainable AI based on EKG
- Use of EKG and LLMs for search and recommendations
Submission
Manuscripts should be submitted in PDF format with 6 pages of content , plus references. Please follow two-column CEUR style template (https://ceur-ws.org/Vol-XXX/) for paper submissions .
Link for paper submission: https://easychair.org/conferences/?conf=ekgllm2023
Camera-Ready Paper Submission and Registration
Authors of accepted papers should prepare a camera-ready (final) version of their paper and submit it using the EasyChair system no later than Sunday, October 1, 2023. Please email the camera ready version(PDF as well as editable versions (doc/latex)) to [email protected] , [email protected], [email protected] and [email protected].
Each accepted paper requires at least one author to perform in person registration using the link https://uobevents.eventsair.com/cikm2023/cikmauthpreandmain and be presented at the workshop in-person in order to include and publish the paper in the workshop proceedings.
Preparation of Camera Ready Paper
Authors are advised to address the comments of the reviewers in the camera-ready version suitably.
Camera Ready version should be prepared using the two-column CEUR style template (https://ceur-ws.org/Vol-XXX/) and it must adhere to the instructions specified at : https://ceur-ws.org/HOWTOSUBMIT.html#CEURART
CIKM 2023 Workshop on Enterprise Knowledge Graphs Using Large Language Models
22nd October 2023,University of Birmingham, UK

About the Workshop
Knowledge graphs are used for organizing and connecting individual entities to integrate the information extracted from different data sources. Typically, knowledge graphs are used to connect various real-world entities like persons, places, things, actions, etc. For the knowledge graphs created using the enterprise data, the knowledge graph entities can be of different types—static entities (e.g., people, projects), communication entities (e.g., emails, meetings, documents), derived entities (e.g., rules, definitions, entities from emails), etc. The graphs are used to connect these entities with enriched context (as edges and node attributes) and used for powering various search and recommendations applications.
With the advent of large language models, the whole lifecycle of knowledge graphs involving –information extraction, graph construction, application of graphs, querying knowledge graphs, using the graph for recommendations, etc., — is impacted. With large language models such as GPT, LLaMA, PALM, etc., entity and relationship extraction can be improved. Similarly, one can answer different types of queries using LLMs which were very difficult without them. This workshop is about improving the enterprise knowledge graphs and its applications using large language models.
Enterprise graphs can be of different scopes—whether it contains data from individual users/customers, a sub-organization, or the whole enterprise. This workshop will also cover various privacy and access control related issues which are typical for any enterprise graph. These include privacy preserving federated learning, using LLMs to extract information from private data, querying the knowledge graph in a privacy preserving manner, etc.
Workshop Objectives, Goals, and Outcomes
Knowledge graphs can integrate diverse data sources and provide a holistic view to the downstream applications. By virtue of being structured, knowledge graphs offer transparency and interpretability to the search and recommendations applications. As per one prediction, this connected data with semantically enriched context applications and graph mining will grow 100% annually. This workshop is about creating and using knowledge graphs on the enterprise data. This data is the internal data of the enterprises—of their employees and/or their customers. Unlike the graphs of open-web entities, enterprise knowledge graphs (EKG) connect the entities specific to the enterprises. For example, all the employee emails, meetings, documents, projects, etc., can be used to create a graph and this graph can be used to summarize the interaction between two employees, identify close collaborators, identify documents which should be attached to an email, documents associated with a project, etc. Similarly, there can be a knowledge graph of items, suppliers, teams, regions, etc., and the graph can be used to recommend suppliers for a particular requirement.
In this workshop we will be covering how large language models can help with the construction and usage of these enterprise knowledge graphs. This involves improving all the aspects of EKG workflow using large language models: entity extraction, entity enrichment, EKG construction, querying EKG for search and recommendations, scenario specific EKG, etc. Besides the well-known challenges associated with the knowledge graphs, EKGs have other issues—how to extract entities from private enterprise data? how to use large language models in a privacy aware manner? how to create relationships between different entities while preserving privacy? how to create EKG with internal (e.g., employees) data and external (e.g., suppliers) data? how is access control maintained in an EKG where data is from different divisions of the enterprise? how are the enterprise recommendations application different compared to, say, movie or a product recommendations? how can one integrate EKG with large language models for a particular application? etc. To ensure privacy and separation of access one may need to use federated graph learning while developing applications over EKGs. How to use federated learning in large language models? Through this workshop we would like to highlight research issues specific to the integration of the enterprise knowledge graphs with large language models and associated applications. By bringing together the researchers (from academia as well as industry) and practitioners (mainly from industry) we want to achieve that.
Workshop Themes
- Enterprise Knowledge Graph (EKG) design and Implementation
- Scalable extraction of enterprise entities using LLMs
- Building EKGs for specific domains or applications
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) algorithms to build EKGs.
- Relationship extraction using large language models
- Federated graph learning with LLMs
- Privacy in graph algorithms
- Privacy preserving graph construction and mining
- Semantic reasoning based on deep learning on graph
- Industrial applications of EKGs: banking, financing, retail, healthcare, medicine, etc.
- Explainable AI based on EKG
- Use of EKG and LLMs for search and recommendations
Target Audience
Researchers and Practitioners from industry and academia. The practitioners and researchers from industry are likely to present their domain, graphs they are building using LLMs, for various applications, whereas folks from academia are likely to identify research problems of common interest and advice appropriately.
Balambiga Ayappane
Balambiga Ayappane is a full-time Research Student at IIIT Bangalore. She is currently focusing on Data Science and Security. She has completed her B.E in Information Science and Engineering from PES Institute of Technology, Bangalore. Her areas of interest include Blockchain and Information Security.
Aparna M
Aparna M is a full time MS by Research student at Web Science Lab. She holds a Bachelor’s degree in Information Science engineering from VTU. She has 2 years of work experience in Middleware development for supply chain management. Her areas of interest include Natural Language processing, NLP in Indian and Low-resource languages and Semi-supervised learning.
For more, please visit her LinkedIn profile.
Publications
- M. Aparna, Sharath Srivatsa, G. Sai Madhavan, T. B. Dinesh, and Srinath Srinivasa. AI-based Assistance for Management of Oral Community Knowledge in Low-Resource and Colloquial Kannada language. International Conference on Big-Data-Analytics in Astronomy, Science and Engineering, BASE 2023, Springer LNCS. [to-appear]
- Sharath Srivatsa, Aparna M, Sai Madhavan G, and Srinath Srinivasa. 2024. Knowledge Management Framework Over Low Resource Indian Colloquial Language Audio Contents. In Proceedings of the 7th Joint International Conference on Data Science & Management of Data (11th ACM IKDD CODS and 29th COMAD) (CODS-COMAD ’24). Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA, 553–557. https://doi.org/10.1145/3632410.3632483
- Aparna M and Srinath Srinivasa. 2023. Active learning for Named Entity Recognition in Kannada. TechRxiv. Preprint. https://doi.org/10.36227/techrxiv.24580582.v1