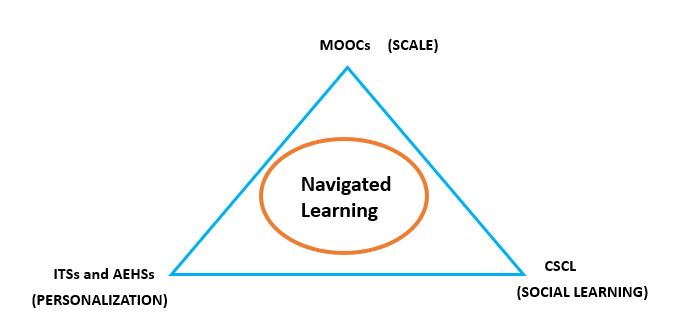
Figure 1: Navigated Learning
Navigated Learning is a new paradigm of learning that aims to balance the three independent requirements: Scale, Personalization and Social Interactions. Please see figure 1 that shows parallels among the concepts that are technological solutions and the three requirements of learning.
This is achieved by representing learning as situated within an abstract “competency space,” and computing semantic embeddings of learning objects and learners into the competency map. The competency map is organized as a progression space– which is a metric space with a partial order. Here, not only is there a notion of “distance” between any two points, but also an element of “progress”. These embeddings can be computed for any semantic object like learning resources, activities, learners, etc. Each point in the space represents a “competency” or a demonstrable skill that can be acquired by the learner.
A primary element of research into Navigated Learning is to construct a competency map for a given subject area of study and to build semantic embedding models for different kinds of objects relevant to the learning process. Semantic embeddings may take different forms depending on the nature of the object. While some objects can be neatly represented as points in the logical space, other objects may be represented by regions, pathways or other contours in the space. In an organizational setting, objects that are embedded onto this space include not just learning resources and learners, but also departments, projects and other organizational elements that require or work with relevant skill sets represented in the competency map.
Navigated learning is manged by a “Learning Navigator” with which every learner interacts. The Learning Navigator (or just, navigator), continuously interacts with the learning map and the learner to perform the following:
Locate: Based on data about their activities and outcomes from formal assessments, the “Locate” module of the navigator embeds learners in the space, and continuously updates their location. Unlike a geographical space, a learner may have acquired several competencies in the competency space. Thus, their location is not identified by a point, but by a data structure called a Skyline, that is detailed in a later section.
Curate: Once a learner’s location is known, based on their stated goals or recently acquired competencies, a set of further candidate competencies are identified. Curating is based on competency modeling principles, that identifies complementary, supplementary and conflicting competencies.
Mediate: This is the logic by which the navigator navigates the learner by making suggestions. Mediation is based on computing an underlying “Narrative Arc” that computes a semantically coherent and meaningful learning sequence individualized for each learner. Mediation also involves suggesting connections with other learners as well as group learning activities.
This project is sponsored by Gooru Learning.
Team Members:
Dr Aparna Lalingkar (PostDoctorate Research Fellow)
Ms Chaitali Diwan (PhD Research Scholar)
Ms Praseeda Kalkur (PhD Research Scholar)
Mr Naman Churiwala (Research Associate)
Mr Prakhar Mishra (MS Research Scholar)
Mr Shyam Kumar VN (MS Research Scholar)
Publications:
Chaitali Diwan, Srinath Srinivasa, and Prasad Ram.Automatic Generation of Coherent Learning Pathways for Open Educational Resources, In Proceedings of the Fourteenth European Conference on Technology Enhanced Learning (EC-TEL 2019), Springer LNCS, Delft, Netherlands, 16-19 September 2019 (to appear)
Aparna Lalingkar, Srinath Srinivasa, PrasadRam (2019), Characterization of Technology-based Mediations for Navigated Learning, Advanced Computing and Communications, Vol 3 (2), June 2019, ACCS Publications, pp. 33-47. (Paper Link)
Praseeda, Srinath Srinivasa and Prasad Ram “Validating the Myth of Average through Evidences” In: The 12th International Conference on Educational Data Mining, Michel Desmarais, Collin F. Lynch, Agathe Merceron, & Roger Nkambou (eds.) 2019, pp. 631 – 634
Chaitali Diwan, Srinath Srinivasa, and Prasad Ram. Computing Exposition Coherence of Learning Resources, In Proceedings of The 17th International Conference on Ontologies, Databases and Applications of Semantics (ODBASE 2018), Valletta, Malta, October 22-26, 2018, Springer International Publishing.
Lalingkar, A.; Srinivasa, S. & Ram, P. (2018). Deriving Semantics of Learning Mediations, In Proceedings of the 18th IEEE International Conference on Advanced Learning Technologies (ICALT), IEEE, pp. 54-55. (Cited by 1 as per GoogleScholar citation index) (Paper Link)
Sub Projects
- Gooru Algorithms (Deep-end tables)
- Skyline
- Machine Classification of Learning Resource
- Gooru – Narrative Arc towards Digital Empowerment
Details of Project Hosted
SDG Map showing various states in 2 dimensions is here
The competency map with polylines is hosted in the link here
The corresponding learning map for the learner is hosted in the link here