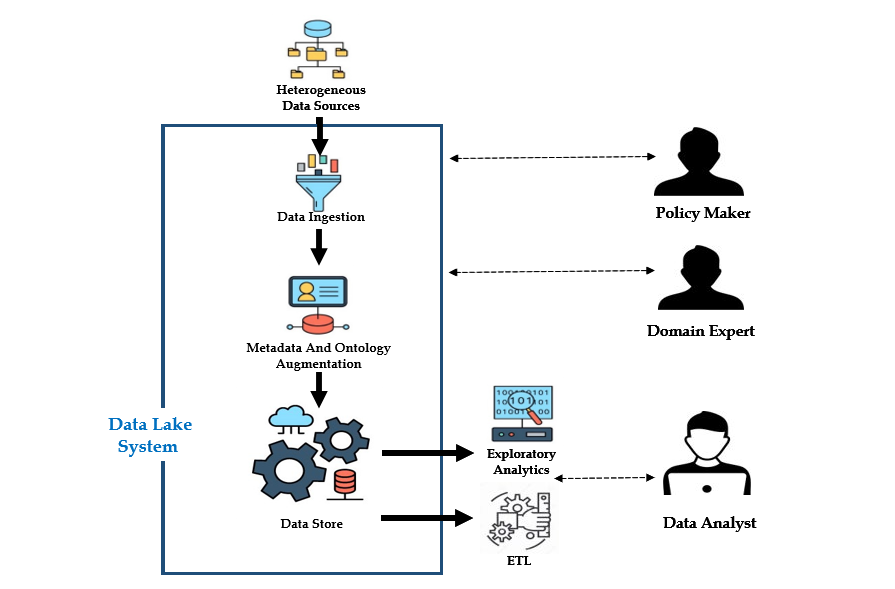
Parichaya project aims at capturing indigenous oral traditional knowledge about sandalwood in rural communities and making it available through an interface that can enable users to interact with audio content to support broader cultural awareness, decision-making, cultivation practices and promote community involvement.
Objectives
Sandalwood plays an important role in Indian cultural, religious, and therapeutic practices. It is extremely important to capture relevant indigenous knowledge in rural communities about the tree from aging populations, support preservation and renew cultivation efforts. In addition to this, the verbal knowledge transferred through multiple generations in rural communities is largely uncodified. The project aims at shaping initial ontologies for a knowledge base about sandalwood.
The Parichaya application contains two interfaces;
- The first interface enables browsing the content using frequent keywords and their context words, representing critical aspects of information in the corpus and providing a good viewpoint of the content
- The second interface supports question-answering, where a user can post a question, get the summary answer, and listen to the audio contents with answers to the question.
Funding Agency
Mphasis F1 foundation
Demos
Parichaya interface : http://103.156.19.244:33404/
(username: guest, password: guest123)
Parichaya demo video :
Publications
Sharath Srivatsa, Aparna M, Samarth P, Malavika V, and Srinath Srinivasa. 2025. Parichaya: Rural Colloquial Knowledge AI Interface. In Proceedings of the 8th Joint International Conference on Data Science & Management of Data (12th ACM IKDD CODS and 30th COMAD) (CODS-COMAD ’25). Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA. [to appear]